VIENNESE SUBURBAN INNS AND THEIR INNKEEPERS UNTIL THE 1950s


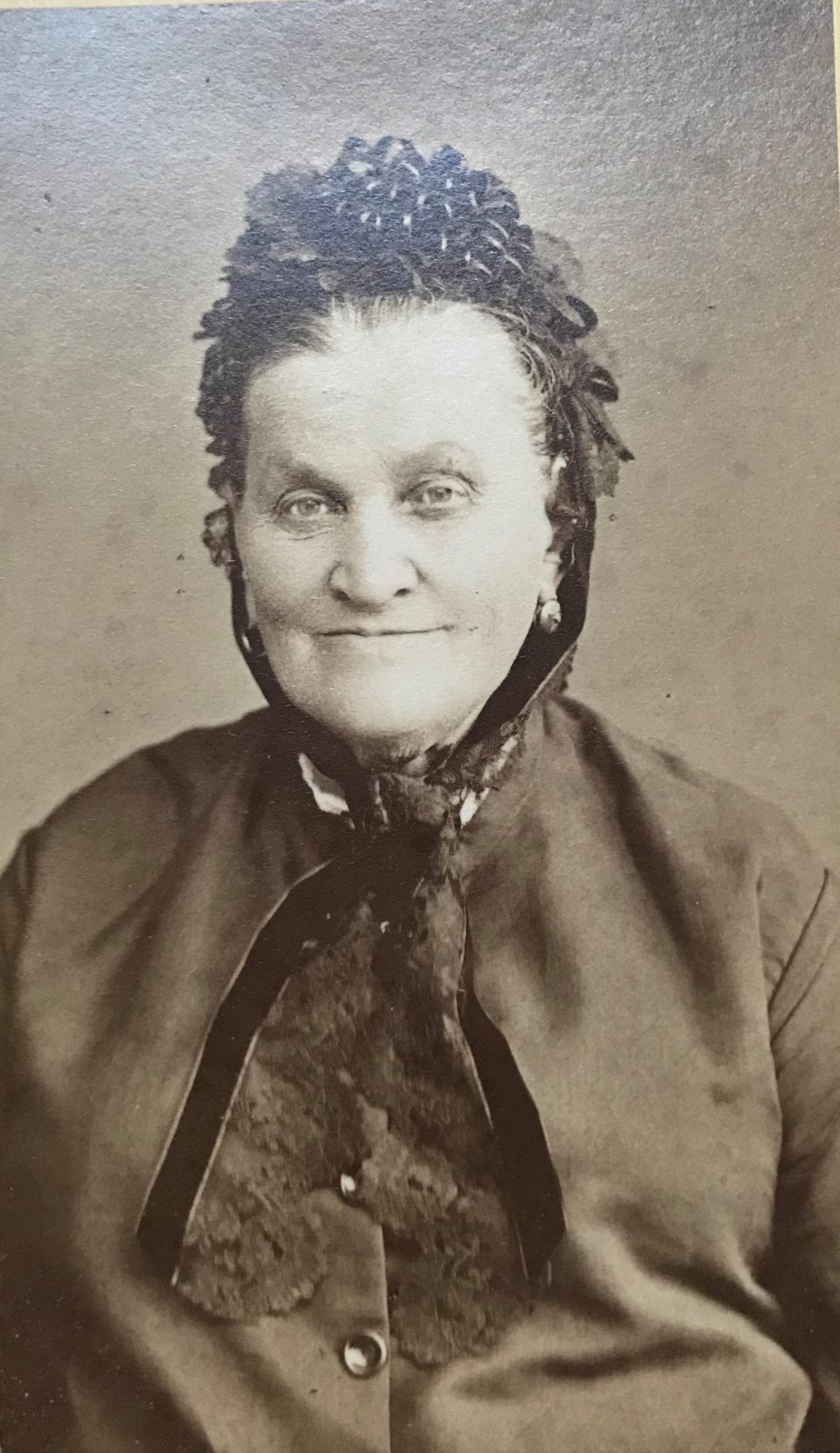
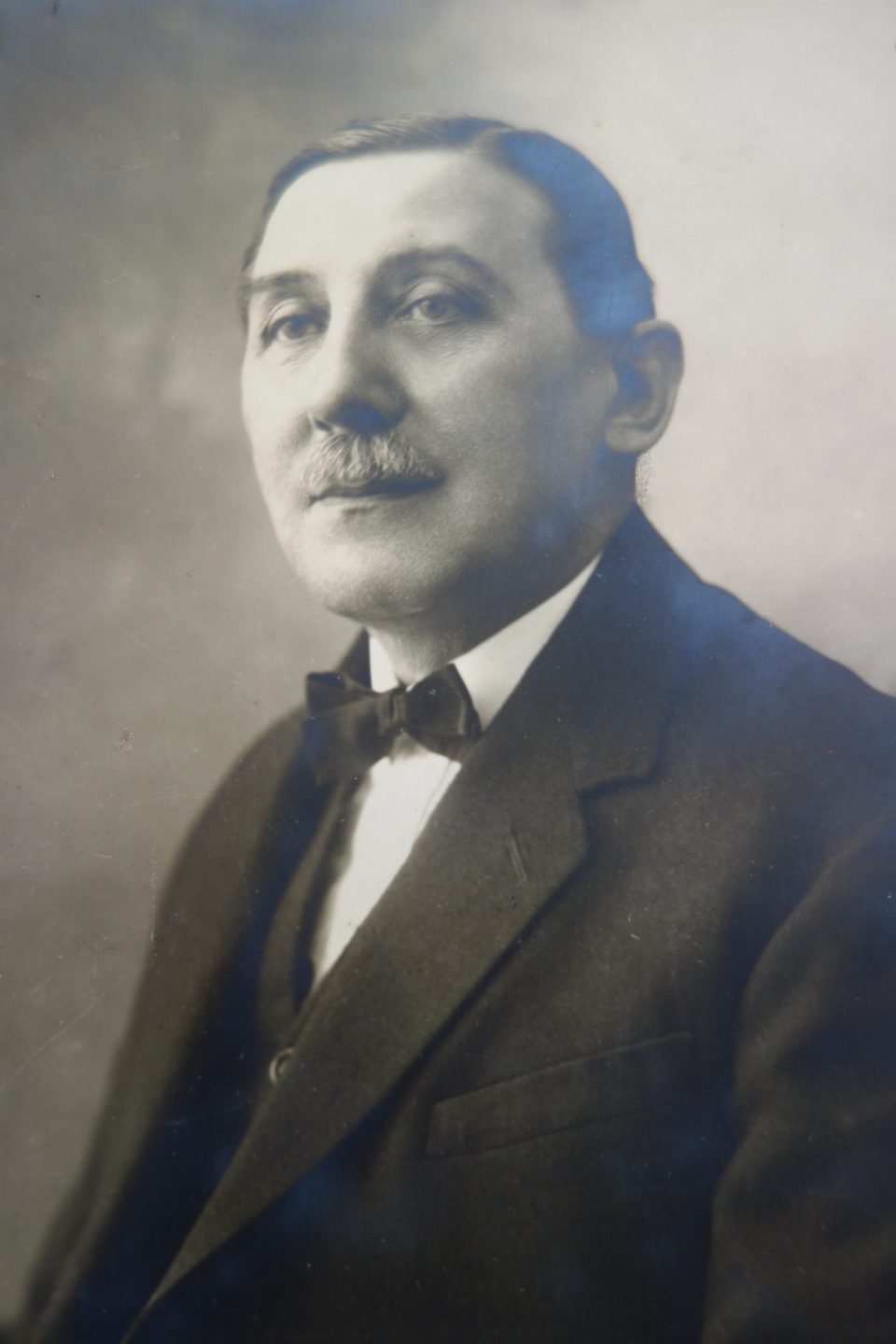
My great-great-grandmother Magdalena Ühlein, innkeeper in Nußdorf (1885) Anton Kainz, my great-grandfather, innkeeper in the Viennese suburb Währing
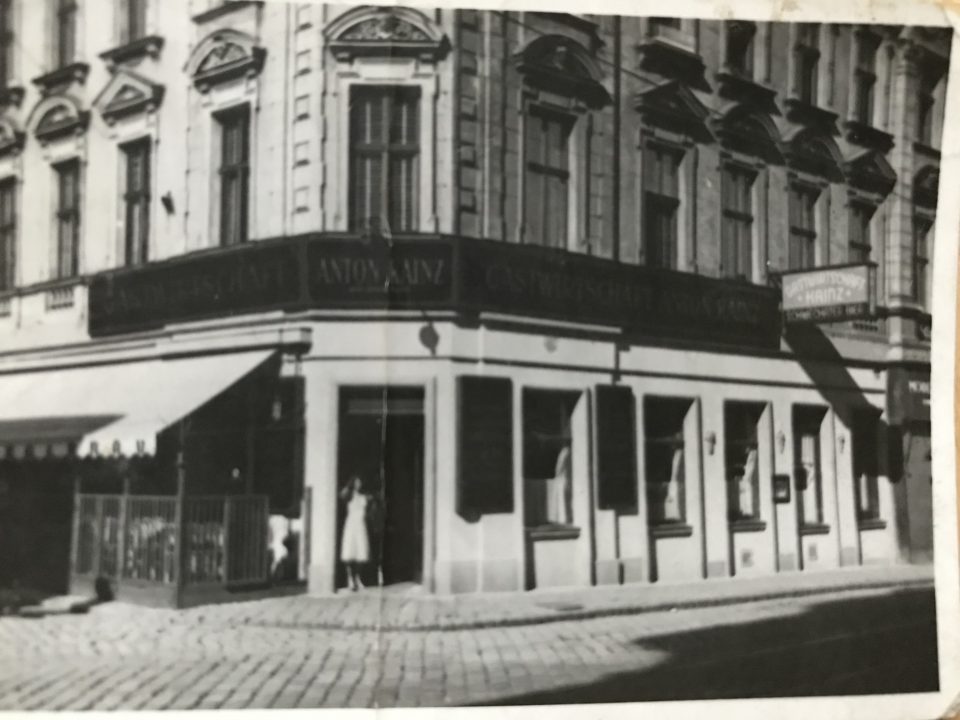
Anton Kainz senior, my great-grandfather, was the innkeeper in the outer suburb of Vienna: Währingerstrasse 146 in the 18th district. My grandfather, Toni was raised there and as he was destined to take over the running of the inn, he was trained as a waiter and cook and went abroad to perfect his catering skills working as a waiter and cook in hotels and restaurants in Switzerland and other fashionable destinations of the bourgeoisie of the 1920s. After the early death of his father his mother took over as innkeeper and when Toni fell desperately in love with my grandmother, he married her against the will of his mother. His mother resisted the marriage because she considered Lola, a beautiful Jewish shop girl in a confectionary shop, an inappropriate match for her middle-class son and heir to an inn. Nevertheless the young couple moved into a tiny room above the inn and worked in the inn alongside the grumpy and tyrannical Mrs. Emilie Kainz, the widowed innkeeper. Toni was the manager of the inn since 1931, but his mother remained the innkeeper; a constellation that could never have succeeded. She continuously harassed both of them until they decided to leave and rent a coffeehouse in the 8th district, Josefstadt. Emilie Kainz was born Emilie Ühlein, daughter of the innkeeper Rudolf Ühlein in Nußdorferstrasse 50 in the 9th district. She must have been the prototype of the strict, rough and uncompromising Viennese innkeeper’s wife, as on can see in the photo:
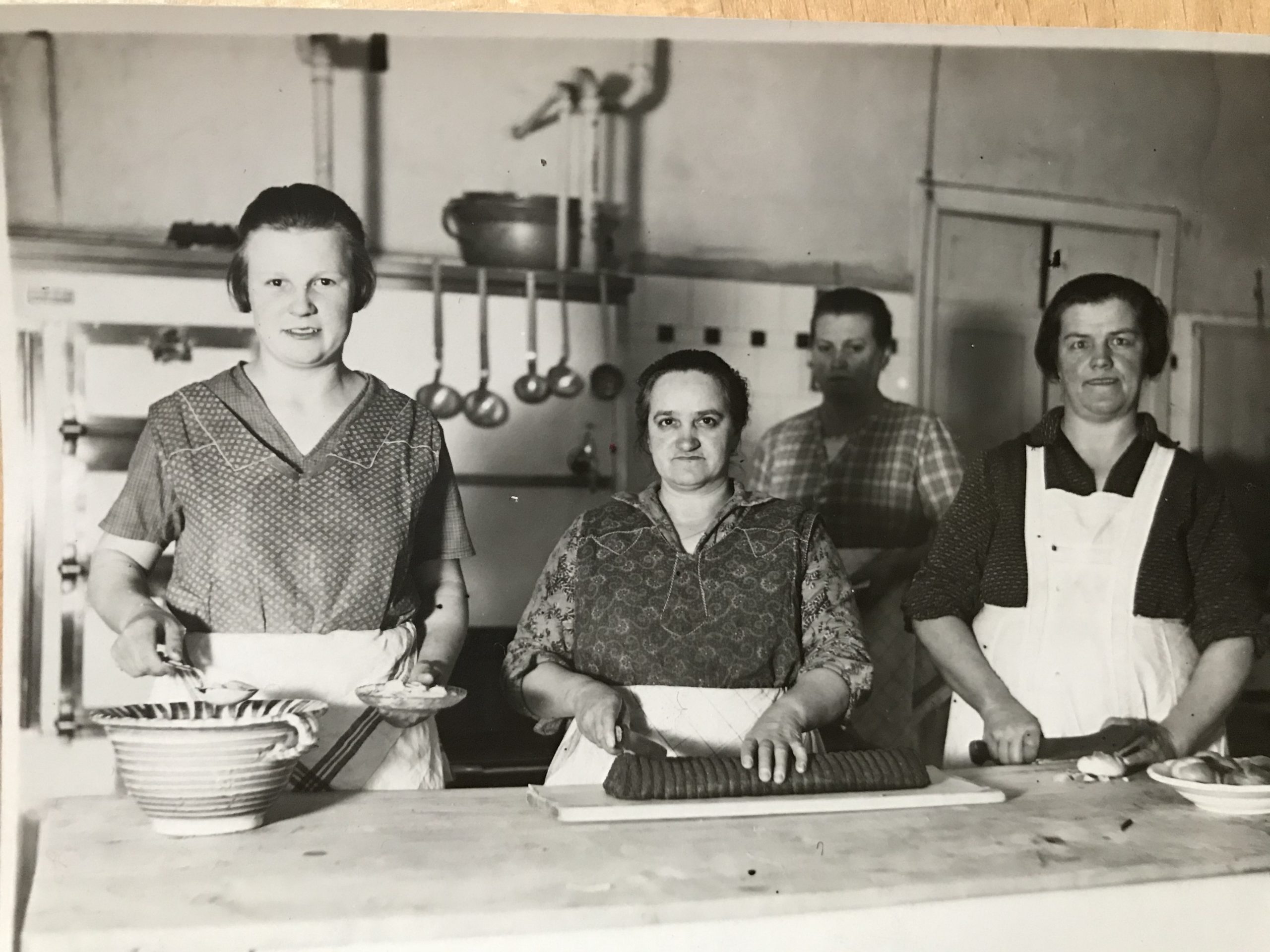

The innkeeper Emilie Kainz in the background in the kitchen of the inn “Anton Kainz”
My grandmother Lola at the entrance of “Anton Kainz” inn, Währingerstrasse 146, Vienna 18
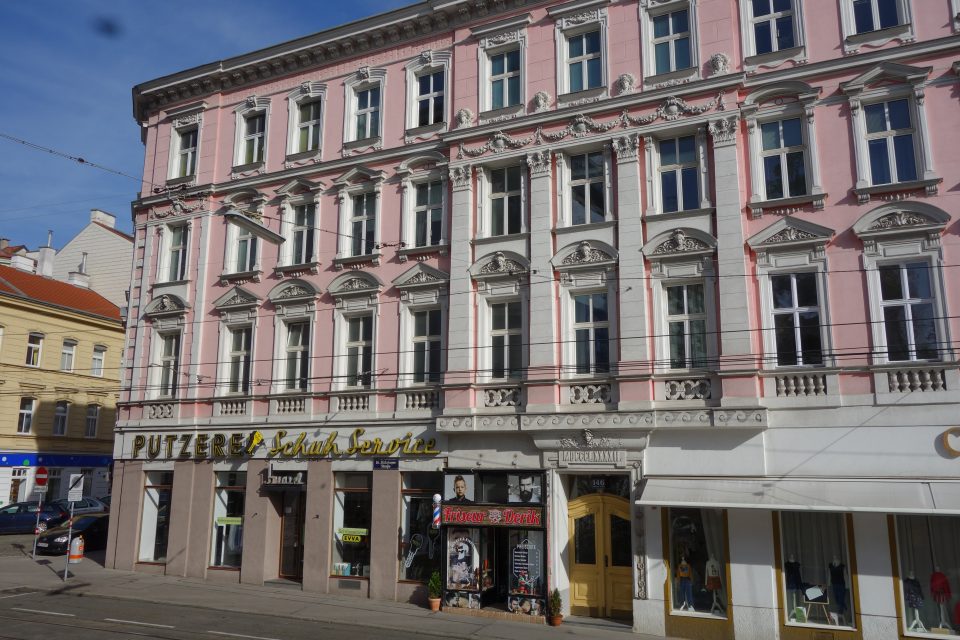
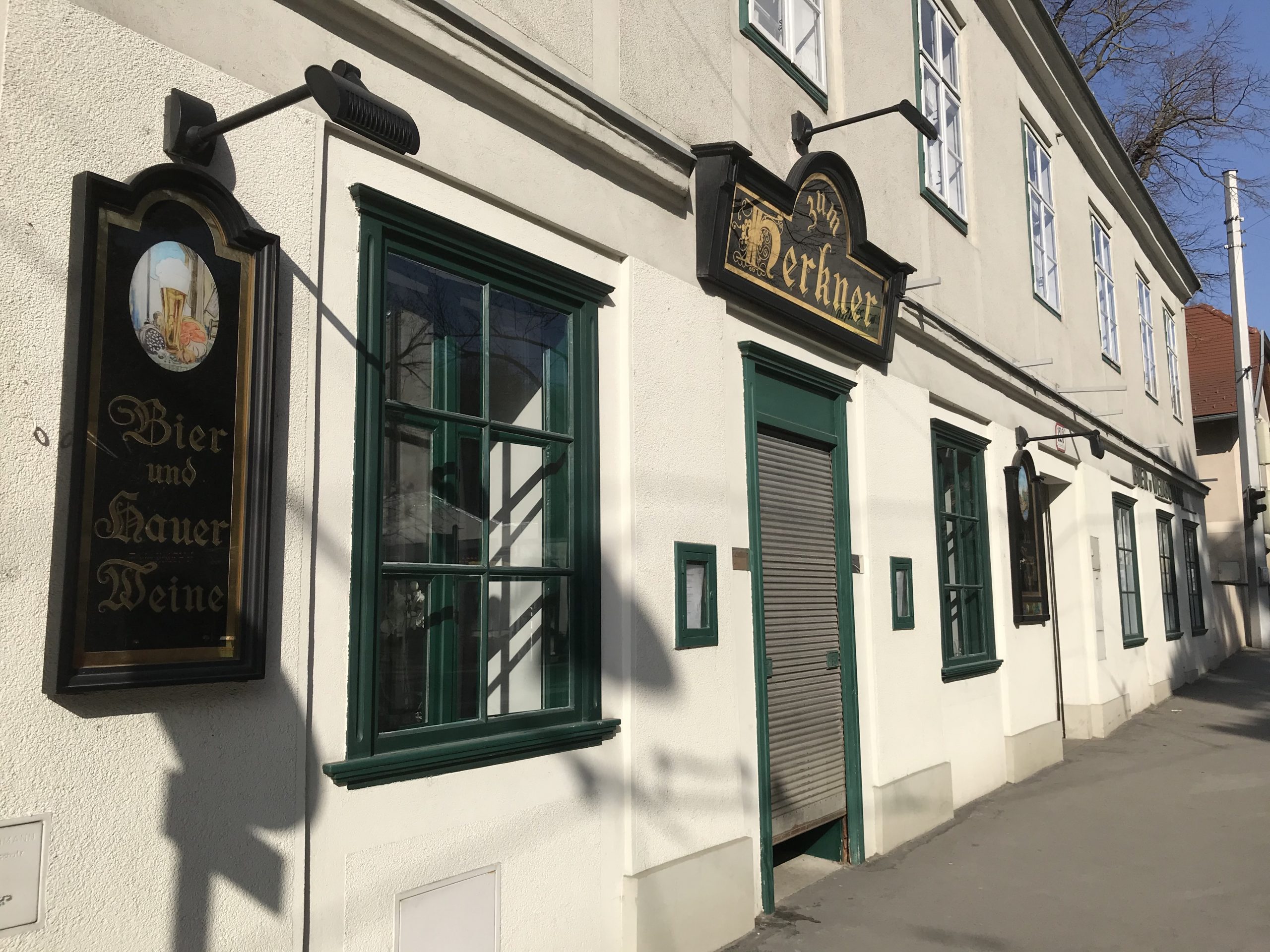
The house today: the inn was replaced by a drycleaner, shoe repair shop and a barber


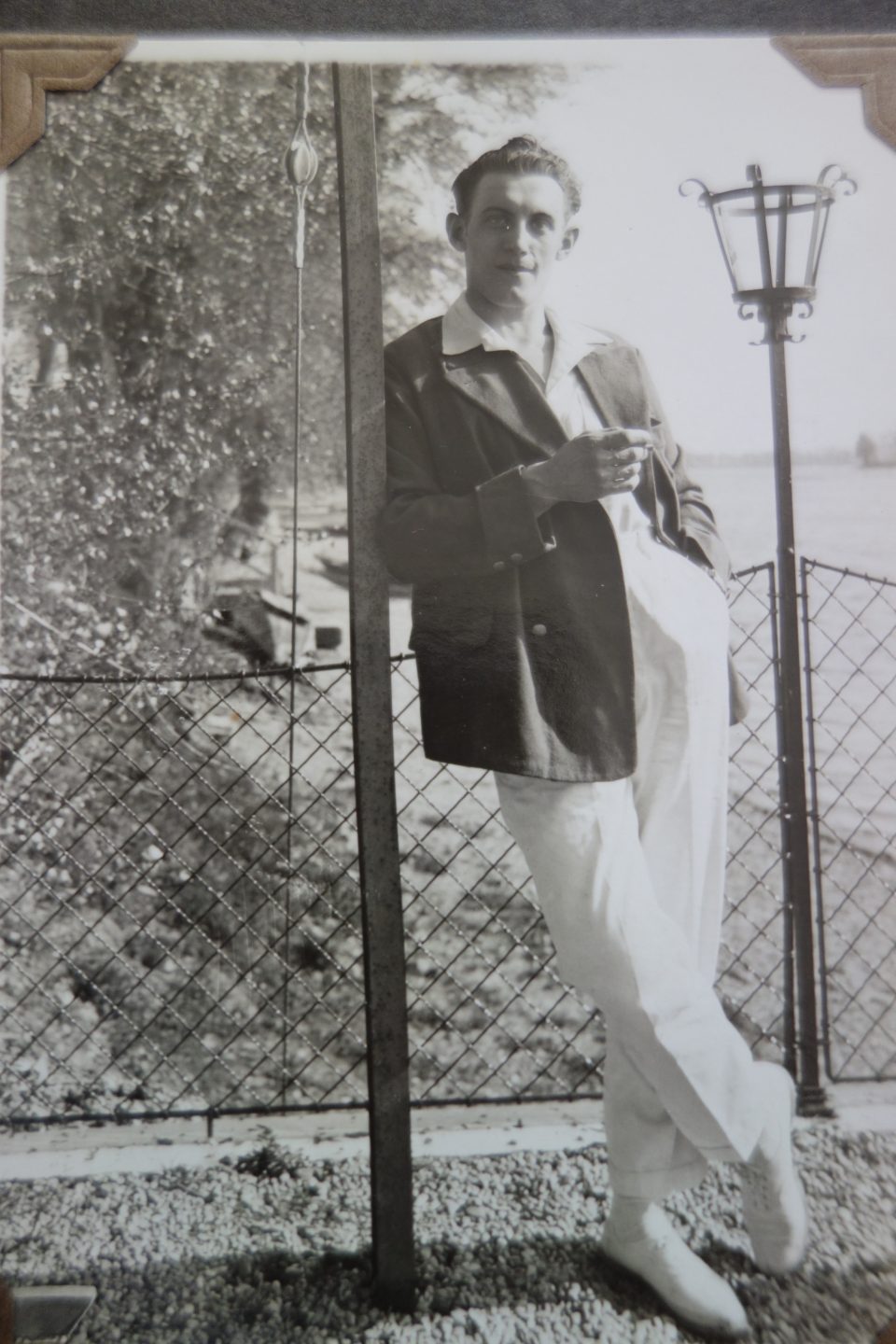
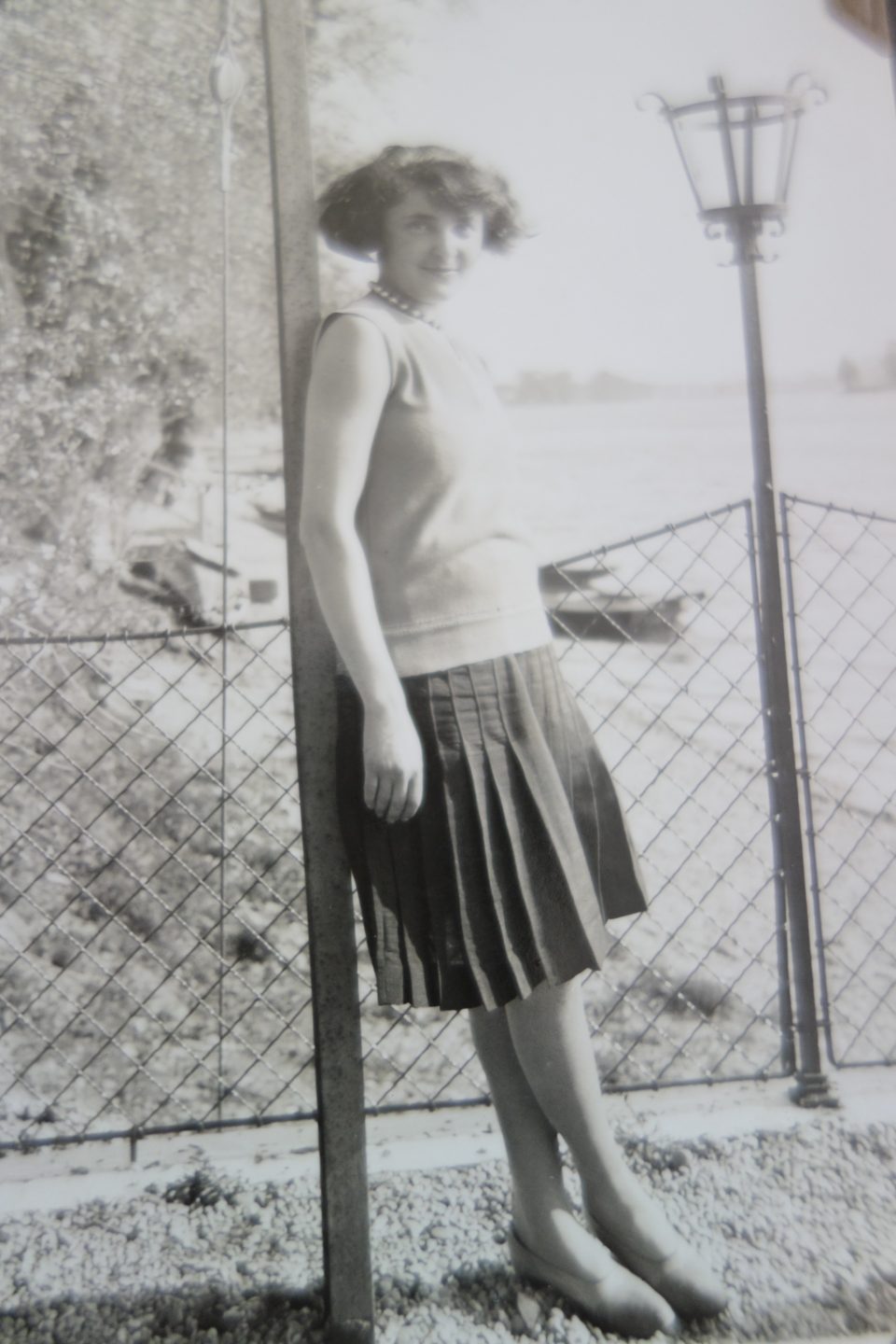
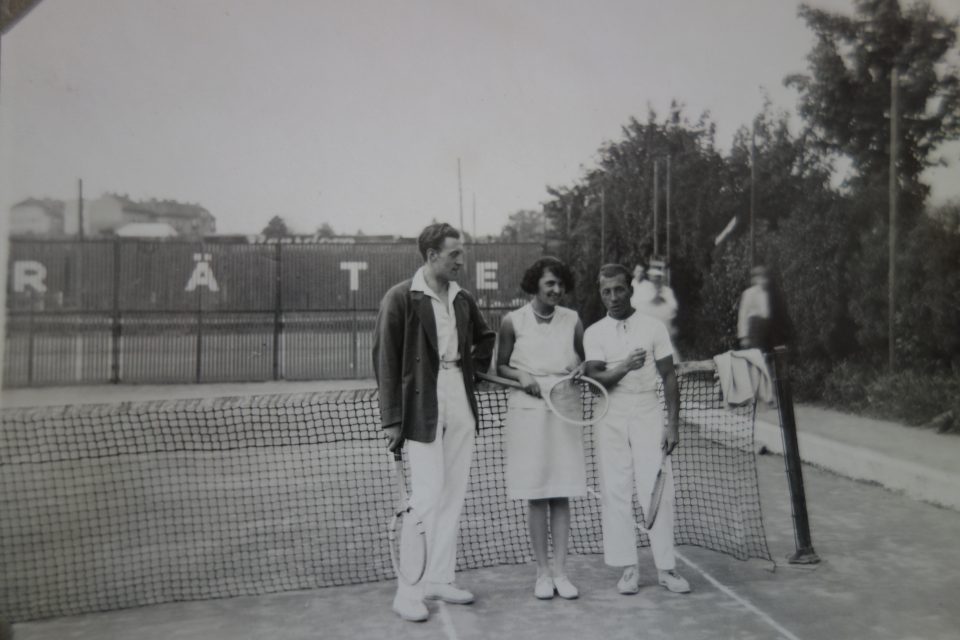
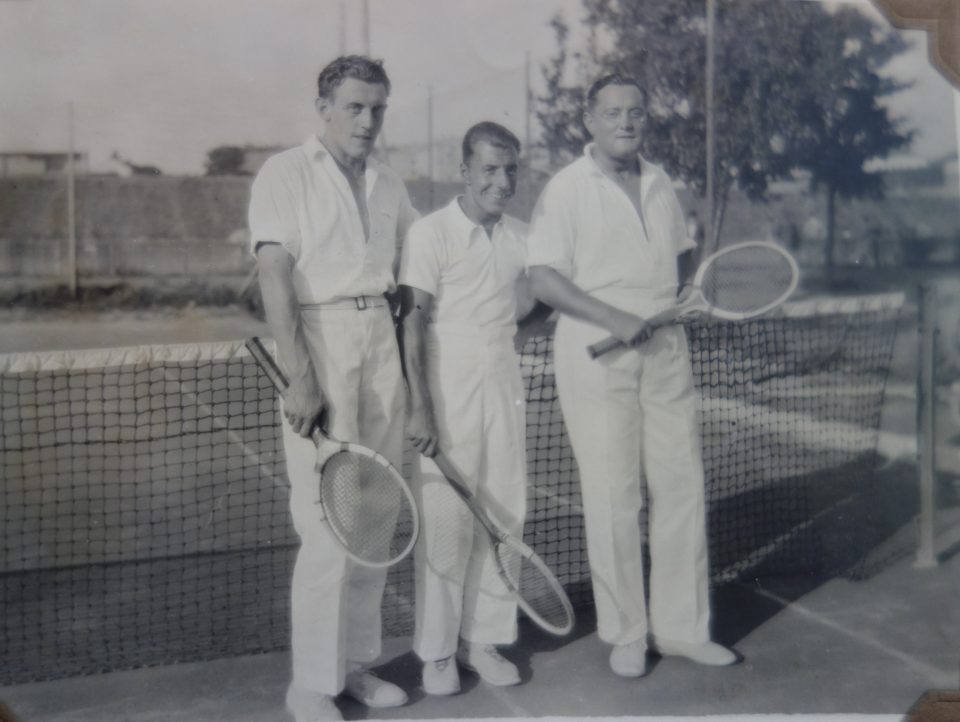
Toni and Lola, the “young bohemians”: They both enjoyed the carefree life of middle class Viennese youngsters in the “Roaring 1920s”.
My grandmother remembered that they both, Lola and Toni, were not cut out for an innkeeper’s career and that they were definitely not gifted entrepreneurs, in fact they were lousy managers. They never seemed to regret not running the “Anton Kainz” inn. Lola immensely enjoyed the company of the guests, but she was no good in the kitchen, where she was supposed to work as long as her mother-in-law was the innkeeper, and Toni loved cooking, but rather for family and friends. He was a rather withdrawn person with lots of aesthetic and philanthropic interests such as philately, music, photography, painting, woodcraft and he loved sport, but not necessarily managing an inn.
…